Global Forum For Indurstrial Devlopment is SPONSORED BY ICO INDIA
- MP Society Registration (Act. 1973 No. 44) 03/27/01/21857/19 (MSME Forum Established Since-2009)

Data mining process is not independent to business process. The impact of data mining can be felt only when there is an impact on the business process. Thus, data mining needs to have relevance to the underlying business process.
Data mining has become an imperative tool in any business process. Today’s technology has improved to store large volume of data unlike few decades back where many considered storing data a wasteful expenditure. The situation has changed now due to several data mining tools available in the market, many of which can mine large volumes of data.

Data mining isn’t a new invention that came with the digital age. The concept has been around for over a century, but came into greater public focus in the 1930s. One of the first instances of data mining occurred in 1936, when Alan Turing introduced the idea of a universal machine that could perform computations similar to those of modern-day computers.
We’ve come a long way since then. Businesses are now harnessing data mining and machine learning to improve everything from their sales processes to interpreting financials for investment purposes. As a result, data scientists have become vital to organizations all over the world as companies seek to achieve bigger goals with data science than ever before.
Data mining is the process of analyzing massive volumes of data to discover business intelligence that helps companies solve problems, mitigate risks, and seize new opportunities. This branch of data science derives its name from the similarities between searching for valuable information in a large database and mining a mountain for ore. Both processes require sifting through tremendous amounts of material to find hidden value.
Data mining can answer business questions that traditionally were too time consuming to resolve manually. Using a range of statistical techniques to analyze data in different ways, users can identify patterns, trends and relationships they might otherwise miss. They can apply these findings to predict what is likely to happen in the future and take action to influence business outcomes.
Data mining is used in many areas of business and research, including sales and marketing, product development, healthcare, and education. When used correctly, data mining can provide a profound advantage over competitors by enabling you to learn more about customers, develop effective marketing strategies, increase revenue, and decrease costs.
Achieving the best results from data mining requires an array of tools and techniques. Some of the most commonly-used functions include:

Data is pouring into businesses in a multitude of formats at unprecedented speeds and volumes. Being a data-driven business is no longer an option; the business’ success depends on how quickly you can discover insights from big data and incorporate them into business decisions and processes, driving better actions across your enterprise. However, with so much data to manage, this can seem like an insurmountable task.
Data mining empowers businesses to optimize the future by understanding the past and present, and making accurate predictions about what is likely to happen next.
For example, data mining can tell you which prospects are likely to become profitable customers based on past customer profiles, and which are most likely to respond to a specific offer. With this knowledge, you can increase your return on investment (ROI) by making your offer to only those prospects likely to respond and become valuable customers.
You can use data mining to solve almost any business problem that involves data, including:
Through the application of data mining techniques, decisions can be based on real business intelligence — rather than instinct or gut reactions — and deliver consistent results that keep businesses ahead of the competition.
As large-scale data processing technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence become more readily accessible, companies are now able to dig through terabytes of data in minutes or hours, rather than days or weeks, helping them innovate and grow faster.
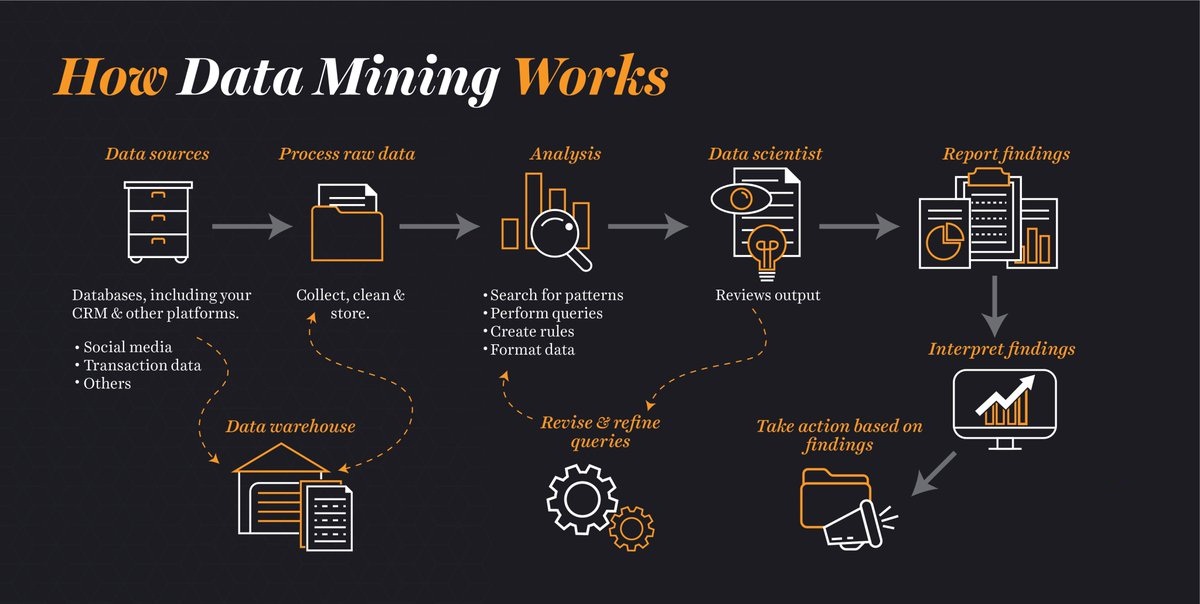
A typical data mining project starts with asking the right business question, collecting the right data to answer it, and preparing the data for analysis. Success in the later phases is dependent on what occurs in the earlier phases. Poor data quality will lead to poor results, which is why data miners must ensure the quality of the data they use as input for analysis.
Data mining practitioners typically achieve timely, reliable results by following a structured, repeatable process that involves these six steps:

Organizations across industries are achieving transformative results from data mining:
Groupon aligns marketing activities — One of Groupon’s key challenges is processing the massive volume of data it uses to provide its shopping service. Every day, the company processes more than a terabyte of raw data in real time and stores this information in various database systems. Data mining allows Groupon to align marketing activities more closely with customer preferences, analyzing 1 terabyte of customer data in real time and helping the company identify trends as they emerge.
Air France KLM caters to customer travel preferences — The airline uses data mining techniques to create a 360-degree customer view by integrating data from trip searches, bookings, and flight operations with web, social media, call center, and airport lounge interactions. They use this deep customer insight to create personalized travel experiences.
Bayer helps farmers with sustainable food production — Weeds that damage crops have been a problem for farmers since farming began. A proper solution is to apply a narrow spectrum herbicide that effectively kills the exact species of weed in the field while having as few undesirable side effects as possible. But to do that, farmers first need to accurately identify the weeds in their fields. Using Talend Real-time Big Data, Bayer Digital Farming developed WEEDSCOUT, a new application farmers can download free. The app uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to match photos of weeds in a Bayer database with weed photos farmers send in. It gives the grower the opportunity to more precisely predict the impact of his or her actions such as, choice of seed variety, application rate of crop protection products, or harvest timing.
Domino’s helps customers build the perfect pizza — The largest pizza company in the world collects 85,000 structured and unstructured data sources, including point of sales systems and 26 supply chain centers, and through all its channels, including text messages, social media, and Amazon Echo. This level of insight has improved business performance while enabling one-to-one buying experiences across touchpoints.
These are just a few examples of how data mining capabilities can help data-driven organizations increase efficiency, streamline operations, reduce costs and improve profitability.

The future is bright for data mining and data science as the amount of data will only increase. By 2020, our accumulated digital universe of data will grow from 4.4 zettabytes to 44 zettabytes. We’ll also create 1.7 megabytes of new information every second for every human being on the planet.
Just like mining techniques have evolved and improved because of improvements in technology, so too have technologies to extract valuable insights out of data. Once upon a time, only organizations like NASA could use their supercomputers to analyze data — the cost of storing and computing data was just too great. Now, companies are doing all sorts of interesting things with machine learning, artificial intelligence, and deep learning with cloud-based data lakes.
For example, Internet of Things and wearable technology have turned people and devices into data-generating machines that can yield unlimited insights about people and organizations — if companies can collect, store, and analyze the data fast enough.
There will be about >20 billion connected devices on the Internet of Things (IoT) by 2020. The data generated by this activity will be available on the cloud, creating an urgent need for flexible, scalable analytics tools that can handle masses of information from disparate datasets.
Cloud-based analytics solutions are making it more practical and cost-effective for organizations to access massive data and computing resources. Cloud computing helps companies quickly gather data from sales, marketing, the web, production and inventory systems, and other sources; compile and prepare it; analyze it; and act on it to improve outcomes.
Open source data mining tools also afford users new levels of power and agility, meeting analytical demands in ways many traditional solutions cannot and offering extensive analyst and developer communities where users can share and collaborate on projects. In addition, advanced technologies such as machine learning and AI are now within reach for just about any organization with the right people, data, and tools.
As the importance of data analytics continues to grow, companies are finding more and more applications for Data Mining and Business Intelligence. Here we take a look at 5 real life applications of these technologies and shed light on the benefits they can bring to your business.
In order for data to really be valuable to an organization, you need to be able to discover patterns and relationships within that data. That’s what data mining does. Those connections and insights can enable better business decisions. Data mining can also reduce risk, helping you to detect fraud, errors, and inconsistencies that can lead to profit loss and reputation damage. Different industries use data mining in different contexts, but the goal is the same: to better understand customers and the business.